POA TUTORS ONLINE
Master POA with a hand-picked, up-to-date, experienced tutor and excel in the subject – from the comfort of home.
You Might Have Seen Us On






“
CALEB HO, B.Acc
Founder, Master Principles of Accounts Technologist, Educator, Designer
100,000
Our Goal Is To Reach 100,000 Students To Thrive In Accounting
I’ve struggled as an accounting undergraduate in NTU – without any background in accounting, having done pure humanities in ACJC.
Master POA is not just a cheat code. It’s a way of mastering accounting concepts that will ensure your learning sticks and becomes sustainable, while turning your understanding into a skillset useful well beyond the exams.
We’ll learn that here, together. Traditional classrooms are too format-focussed and slow. We are nimble and effective, and the way we learn must be as such as well.
Together, with 100,000 of us, we can change the way we learn accounting into something more fun, more rewarding and more productive.
What Most Students Do
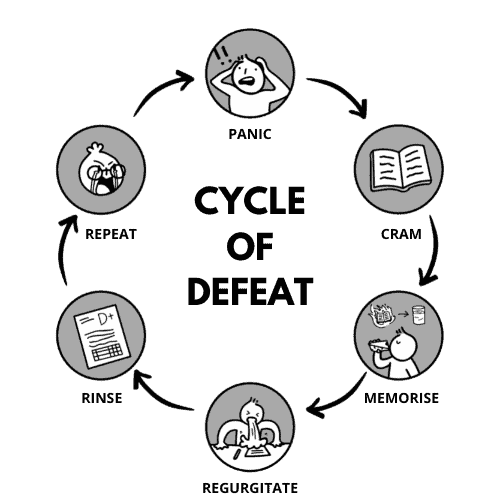
In the decades teaching this subject, we observed how students painfully struggle to memorise steps, journal entries and formats to clear their WAs, MYEs and EOYs – only to achieve dismal results.
Now, the problem with this approach is that with each upcoming test, there are brand new chapters, concepts and formats tested. With each assessment, means new rounds of late-night memorisation and regurgitation for the next day.
After the test, the problem snowballs further. You never seem to ‘get it’ or feel you are too far off to catch up with the new topics as they build on previous’ concepts and foundations.
This rinse-repeat approach becomes a cycle of defeat, until the brain is exhausted from memorising something you really tried but cannot understand.
A rising resentment grows – every POA class you sit in becomes increasingly “dry, boring and confusing.”
Introducing The LEAP Method
Our proprietary LEAP METHOD uses the established J-curve learning framework. The initial part of the “J” creates a reduction in satisfaction as the student weans from the memorising approach. With time, effort, and support does the student move through the initial downward part of the curve, and reach the upward portion, which results in remarkable, repeatable results.
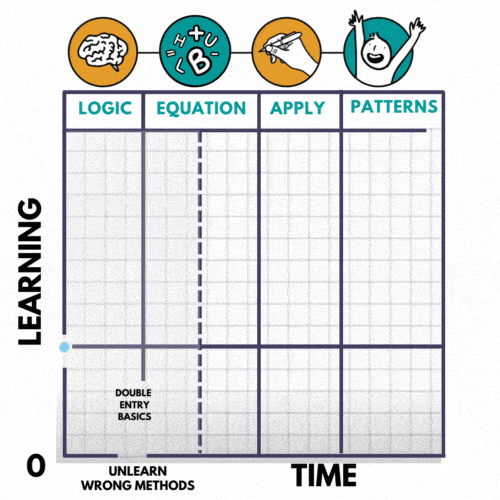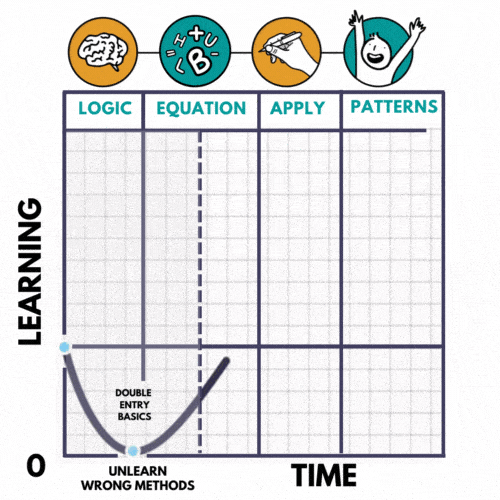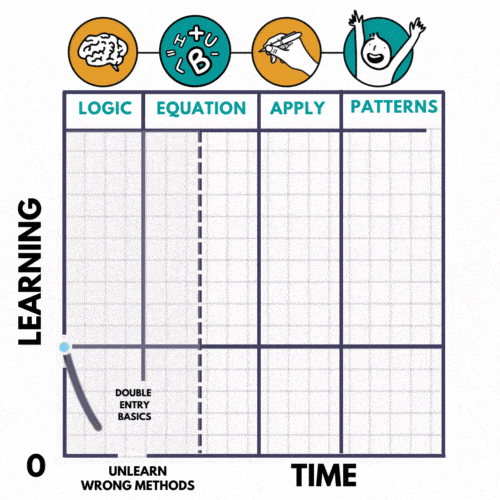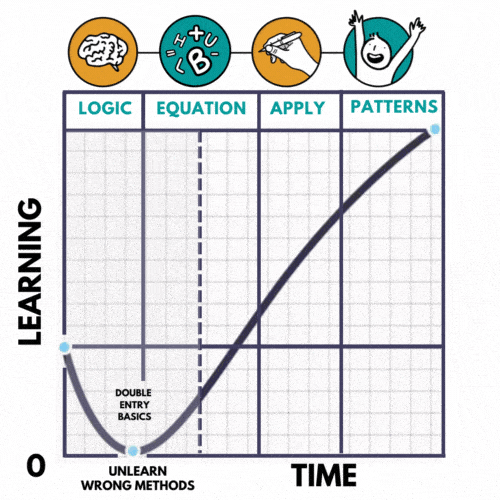
Here’s how it works
- LOGIC
Breakdown each exam question into a logical sequence of events and making it relate to real life - EQUATION
Construct the HBUL equation and solve to find the exact item the examiner is testing for. - APPLICATION
Present the equations in journal entries and financial statements in chronological order. - PATTERN RECOGNITION
Cultivate your ability to recognise HBUL equations across multiple chapters efficiently and effectively and reduce revision time by more than 75%!
Your Journey to Mastering POA Starts In Just
4 Simple Steps

Tell us about yourself
Let us know where you are at POA and if you need help with double entry basics plus your preferred learning mode.
Get expertly matched
Our program coordinator will pair you up with the perfect tutoring arrangement based on your profile and preference
Get your personalised study plan
Get a crystal clear roadmap to completing the syllabus in time for your exams – with specific timeline and topical coverage.
Embark on your learning journey
Get familiar with your tutor and experience what it is like to learn with Master Principles of Accounts
Here Are 3 Ways You Can Start Learning More About Master POA

SMALL GROUP FACE-TO-FACE COACHING
Up to 4 students per class at Joo Chiat Road with Teacher Joy. Ex-MOE teacher with 30 years experience. Trained in the latest 7086/7 Syllabus

LOOKING FOR INTENSIVE CATCH UP?
Instructor-led 40 x Weekly 1hr Live Classes
Polls, Quizzes & Digital Worksheets
Extensive Video Library With Worked Solutions
Community Support

WEEKLY CLASSES
Small Group Weekly 1.5hr Coaching
Marking and Personalised Feedback
Private Homework Room
Individualised Digital Repositary
Extensive Video Library
Whatsapp Support
Your Instructors
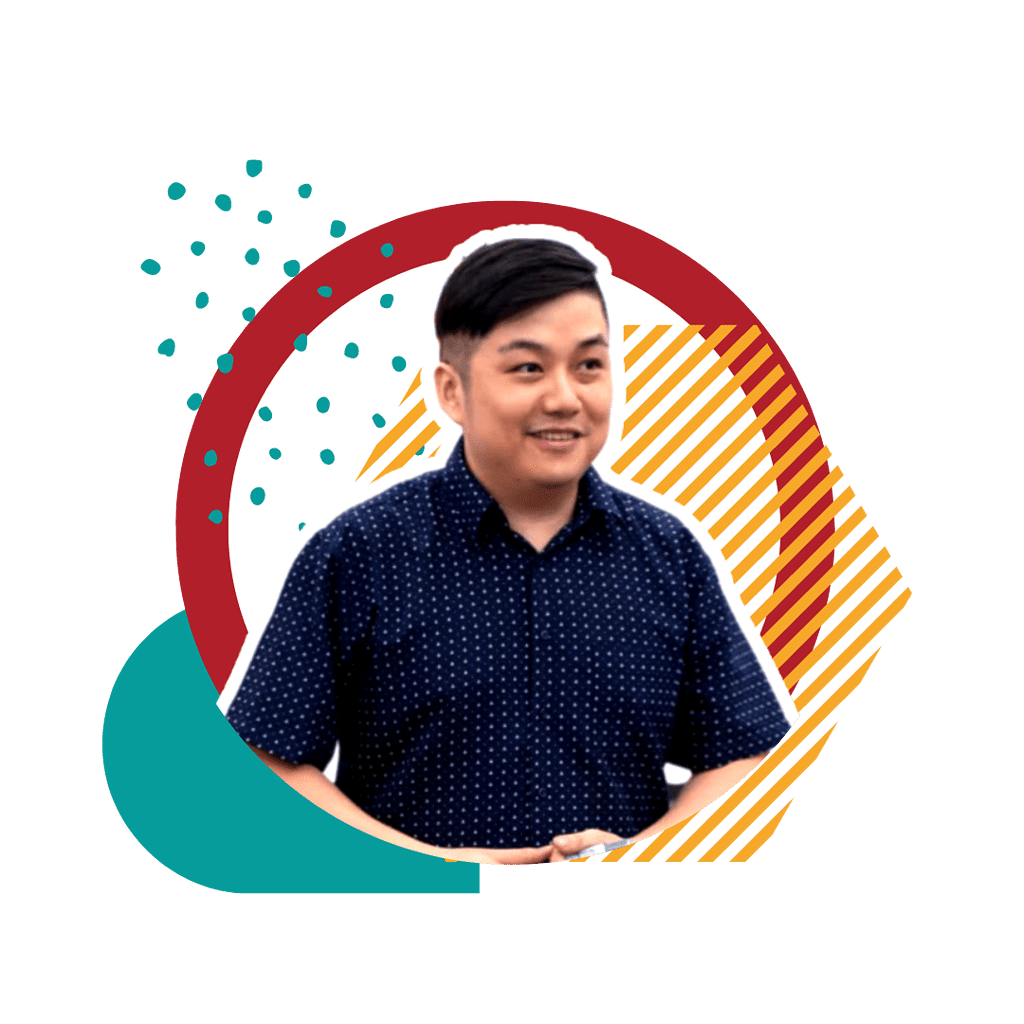

Who’s this Caleb Guy?
Since I love speaking about myself in 3rd person, let’s talk.
Unlike most accounting teachers/educators who teach accounting for a living, Caleb’s been applying accounting and financial concepts since 2008 – mostly in investing, startups in accounting and community events for personal finance.
When Caleb taught his first POA student at age 23, he discovered that the study guides in the bookstores then (and still is in 2024) were dry and un-engaging. He decided to help his own students by publishing his own and since sold over 10,000 copies with raving reviews of how the summaries, exam tips and concise worked examples resonated with the students’ struggles.
For his applied accounting knowledge in real life and small businesses, he’s been featured in numerous interviews and articles in Yahoo!, Dollars and Sense, 1M65, Seedly, The Straits Times, Vulcan Post. He also sat on the boards of Spirit of Enterprise and TEDxSingapore, curating the best ideas and well deserving entrepreneurs to be platformed for recognition.
All of Caleb’s approach towards double entries come from 15 years IN THE TRENCHES building, creating, innovating and simplifying when necessary.
Zero fluff. And 100% real-world and tactical.
And if you haven’t heard of Caleb before, it’s probably because he spends most of his time behind the scenes helping small business owners and non-profits build online learning communities
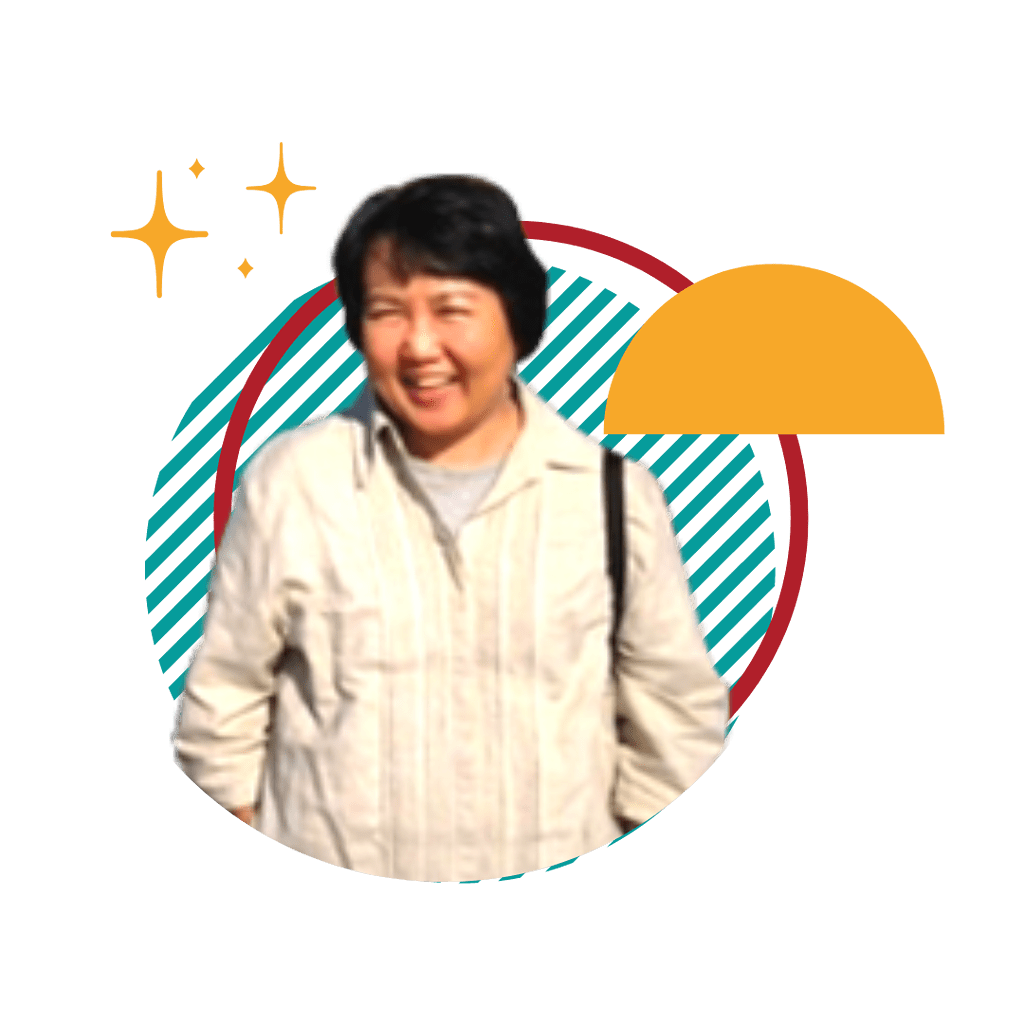

Joy Ang-Shinchi
Teacher Joy is an ex-MOE teacher, has been teaching Principles of Accounts (POA) over a 35 year span, impacting more than 2,000 students in MOE schools. Her array of education accolades include a Bachelor of Commerce, a Diploma in teaching, a Diploma in Film and Television (Script), a Masters Degree in Education and currently pursuing a MA in Creative writing
More importantly, Teacher Joy brings accounting alive via her wide span of interests and experiences in the manufacturing, overseas postings and career guidance in a local university.
Her witty sense of humor, ability to connect with youths and hilarious comebacks attracted a fair share of fans over the years.
Teacher Joy carries with her the most up-to-date NIE pedagogies and is trained in the latest 7086/7087 GCE O/N Level POA Syllabus. She believes strongly in providing students with the tools and support they need to achieve their dreams. As a lifelong learner, she is able to provide career guidance and mentorship.
Take Your First Step To Finally Thrive In Accounting
Let’s Connect You With A Hand-Picked Program Today